Clinical application of liraglutide (2)
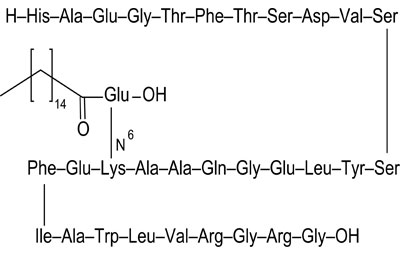
Liraglutide is a synthetic glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog, which was officially launched in 2009 and applied to the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Liragglutide is formed by adding a 16 carbon palmitoyl fatty acid at position 26 of GLP-1 through gene recombination technology, and substituting arginine for lysine at position 34 of GLP-1; These structural modifications increase aggregation and promote the binding of non covalent albumin, thereby inhibiting the degradation of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Therefore, the half-life of liraglutide is far greater than GLP-1, and it can be administered once a day, which has outstanding clinical advantages. Liraglutide (same as exenatide impurities )can effectively prevent the decline of pancreatic islet B cell function, so as to control the long-term stability of blood glucose to reach the standard, and reduce gastrointestinal reactions and hypoglycemia and other adverse drug reactions.
In recent years, with the in-depth study of Liraglutide, it has been found that in addition to treating type 2 diabetes, it plays a beneficial role in controlling the body mass of obese patients, cardiovascular system diseases and nervous system diseases. Its pharmacological effects and clinical applications are expanding. This article summarizes the clinical studies of Liraglutide in the treatment of diabetes, obesity, nervous system diseases, cardiovascular system diseases and mental diseases, and discusses its mechanism of action, with a view to providing reference for the clinical application of Liraglutide.
1. diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic hyperglycemic compensatory disease, which is mainly manifested by decreased insulin secretion and increased liver glucose output. Liraglutide was approved for adult type 2 diabetes in Europe in 2009 and in the United States in 2010. Its hypoglycemic mechanism is mainly to stimulate the proliferation of islet B cells, and to achieve functional regeneration of islets by inhibiting apoptosis. Some studies have shown that liraglutide can inhibit IRS-1 serine phosphorylation in mouse skeletal muscle cells to enhance insulin induced glucose transporter 4 translocation, thereby reducing insulin resistance. Clinically, it is found that Liraglutide can be used as an adjuvant treatment for recurrent type 2 diabetes after metabolic surgery, and its combination has a better therapeutic effect on type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease of islet cell injury mediated by T cells. At present, insulin injection is the main treatment method. There are clinical data showing that liraglutide can be used as a supplementary treatment for type 1 diabetes patients, which can significantly improve blood sugar, reduce the risk of severe hypoglycemia, increase lipid oxidation and thermogenesis to reduce body mass, but increase gastrointestinal adverse reactions. In addition, Liraglutide can also inhibit the formation of glucagon and lipolysis in type 1 diabetes. One study indicated that liraglutide could inhibit the production of human T lymphocytes through JAK-STAT pathway under high glucose conditions γ Interferon, this result suggests that Liraglutide also plays a potential therapeutic role in the immune regulation of type 1 diabetes.
2. Obesity
Obesity is a chronic metabolic disease caused by excessive accumulation of fat caused by genetic, environmental and other factors, which leads to a body mass far beyond normal. At present, most obesity treatment guidelines include the suggestion of combining lifestyle changes with drug treatment. Among them, Liraglutide has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as one of the safe and effective drugs for weight loss, and its effect is better than that of intensive behavioral therapy for obesity alone.
Liraglutide mainly controls obesity by controlling appetite and reducing eating. Its mechanism mainly includes activating GLP-1 receptor in the brain to produce anorexia; At the same time, it regulates intestinal flora and delays gastric emptying to increase satiety. In addition, fmoc-osu it may also reduce body mass and improve obesity by inducing browning of white adipose tissue through soluble guanosine cyclase dependent pathway and activating adenylate cyclase pathway [mouse sc 400 μ g/(kg·d)。 The analysis of clinical data shows that the control of obesity by Liraglutide does not depend on the hypoglycemic effect. It has therapeutic effect on both diabetes and non diabetes patients. Long acting neurotensin and Liraglutide can reverse obesity through melanin dependent pathway, and have better tolerance.
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap