Fmoc Amino Acids | Omizzur

The protection of amino acids in the synthesis of peptides is very important. Many of the common 20 amino acids have active side chains and need to be protected. It is required that these protecting groups are stable during the process, without side reactions, and can be removed after the synthesis.
Protected amino acids are the most raw materials for solid-phase synthesis. Amino acids all contain alpha amino and carboxyl groups, and some of the 20 amino acids also contain side-chain active groups. These active groups need to be protected during the reaction. These groups are removed after the reaction is finished. The most common used is the Fmoc amino acids.
Solid-phase Peptide Synthesis
The synthesis of peptides is controlled by the of different amino acids in a certain order. One difficulty is that the reagents required for reactions can interact with other functional groups that do not join in peptide grafting. such as the free amino group of the N-end amino acid , the free carboxyl group of the C-end, and some active groups in the side chain, especially the SH group. They can all interact with peptide reagents.
In order to obtain peptides with specific order, a correct method of condensation is needed. Before synthesis, these groups must first be blocked to avoid interacting with peptide reagents and generating unnecessary peptide bonds or other bonds. After the peptide bond is formed, the group is removed.
Main Design Ideas for Solid-phase Synthesis of Peptides
Firstly, the carboxyl group of the C- terminal amino acid of the peptide chain to be synthesized is linked to an insoluble polymer resin. Then, the amino acid bound to the solid phase carrier is used as an amino component. Then remove the protective group and react with an excess activated carboxyl component to lengthen the chain.
This step can be repeated many times, including condensation, washing, deprotection, neutralization, and washing. Then we followed by the next round, and reaching the desired final chain length.
Amino Acids that Need To Be Protected
Include: Cys, Asp, Glu, His, Lys, Asn, Gln, Arg, Ser, Thr, Trp, Tyr.
Groups that need to be protected: hydroxyl, carboxyl, mercapto, amino, guanidine, indole, imidazole, etc.
Where Trp can also be unprotected, because indole is stable in nature. Of course, some amino acids may not be protected, such as Asn, Gln, Thr, Tyr.
Fluorene methoxycarbonyl (Fmoc group)
This protective group is stable to acids. It can be removed with a 50% dichloromethane solution of amines such as concentrated ammonia water or 4 mol/L NaOH.
Fmoc group has strong UV absorption. It can be used for peptide synthesis in both liquid and solid phases by pairing with protective groups removed with acids. The advantages of Fmoc group are:
1) Fmoc protected amino acids are very stable to acids, using acids to remove Boc and Z groups, and Fmoc protected amino acids also have good stability.
2) Fmoc protected amino acids can be removed from Fmoc groups using ordinary amines.
The Fmoc group is joined into amino acids in the NaHC03 or Na2C03 through the following reactions. As shown in the image:
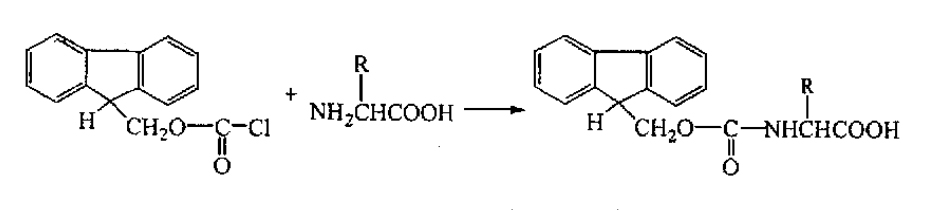
Removal of Amino Acids Protecting Groups
There are many protecting groups for amino acid side chains. The same side chain has many different protecting groups. They can be removed under different conditions. This is of great significance in the modification of cyclic peptides.
Moreover, the side chain protecting group is closely related to the selected method. The liquid and solid phase are different, the BOC and FMOC in the solid phase are also different as we know. In a sense, peptide chemistry is the flexible use and matching of amino acid protecting groups.
Omizzur is currently looking for local high-quality partners, has rich incentive policies for manufacturers or local dealers worldwide. Contact us now .
Copyright © 2020 Omizzur Inc | Terms & Conditions | Privacy Notice | Sitemap